NVR/Port Forwarding
Port Forwarding Luminys Devices
Description
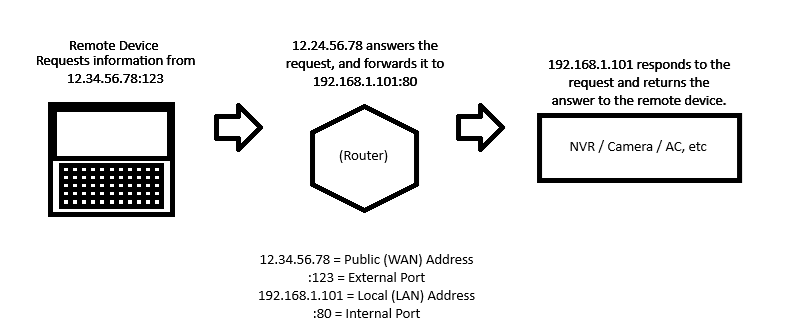
Port forwarding is a technique that directs incoming network traffic from one combination of an external IP address and port number to a specific internal IP address and port number on a private local area network (LAN). This tutorial will go over which ports need to be open to allow remote access to Luminys devices and a generic overview of how to set up port forwarding. Please note that not all routers are the same, so this guide serves to cover the general process only and is not specific to your network.
Prerequisites
- Access to router / firewall administration
Step by Step Instructions
1. Identify the local IP address for the device you are configuring (NVR, Camera, etc)
You can use LumiUtility to scan your local network for Luminys devices and identify their current IP address.
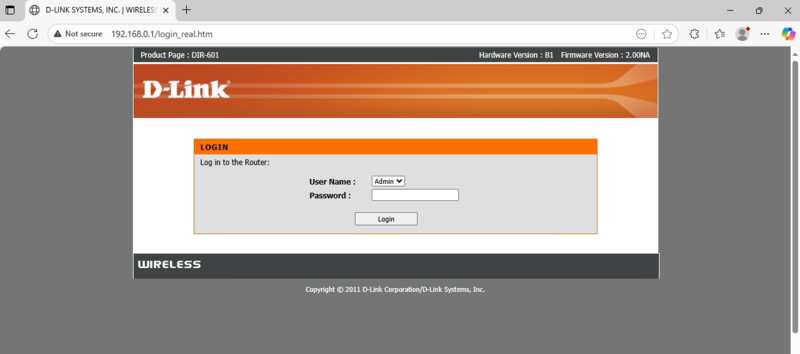
2. Access Your Router's Administration Page.
In most situations, you will be configuring port forwarding through a routers webui. To access this, you need the router's IP address (the "Default Gateway") to log in and make changes. If you need to know your devices default gateway, you can view this information in LumiUtility as well by clicking the details button beside the device.
Open a web browser, type the router's IP address into the address bar, and press Enter. This should take you to a log in screen for the router. If you do not know the login information, check the router for a sticker which may have the details printed on it, otherwise, reach out to your network administrator or internet service provider.
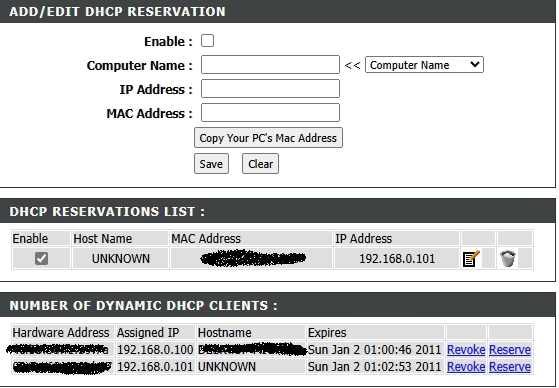
3. Assign a Static Local IP (DHCP Reservation).
If the device's local IP changes, your port forwarding rule will instantly stop working. A DHCP Reservation tells the router to always assign the same IP to your specific device. Navigate to the LAN or Network Settings section of your router, and look for DHCP Reservation, Address Reservation, or Static Lease. Enter the device's MAC Address (a unique hardware ID) and the Local IP Address you want it to always use (the one you identified in Step 1).
Of note, you can also set the IP address as static on the device itself, but setting it via the router is a more secure way to ensure the IP is not recycled to another device should the preferred IP list be exhausted.
4: Configure the Port Forwarding Rule.
Find the section labeled Port Forwarding, Virtual Servers, NAT, or Security within your router's settings. You should find the option to add a New Rule or to create a new entry. You will need to provide the following information:
Name: Give the rule a clear, descriptive name (e.g., "NVR LumiViewer"). Protocol: Select TCP, UDP, or Both, depending on what type of data you are sending over the port. External/WAN Port: The port number traffic enters your network on. Internal/LAN Port: The port number the service on your device uses (often the same as the External Port). Internal IP Address/Destination: Enter the Static Local IP Address of your device (from Step 3).
For example, if you are forwarding an HTTP and RTSP port to use a Luminys device on LumiViewer remotely without having to use P2P, you would forward to ports 80 and 443, so that you can add the device to LumiViewer via the public IP address.
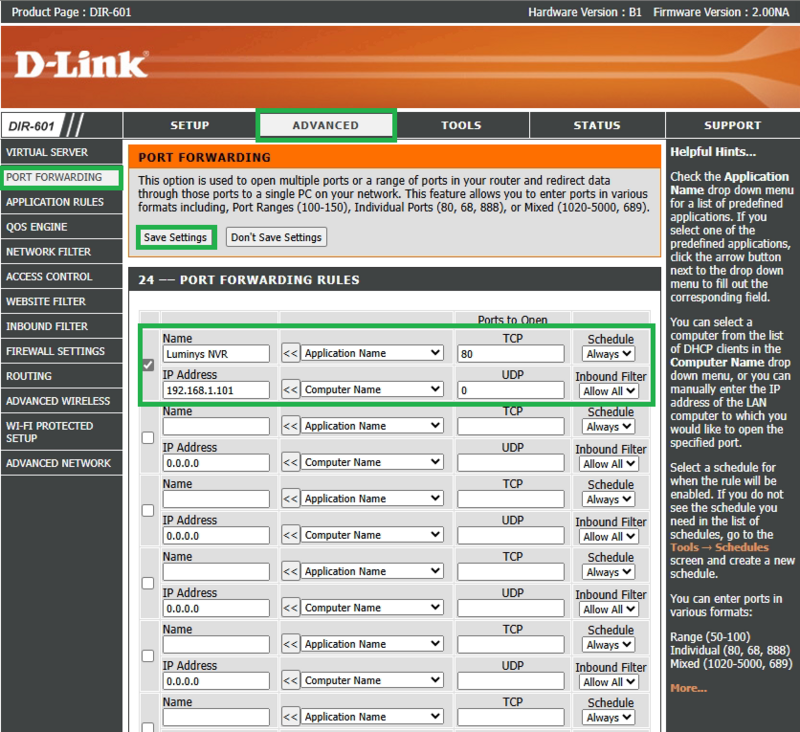
(In this example device, we do not have the option to forward from a different external port to an internal port, but many modern routers will let you. For this router we can only "redirect" the traffic on the same port to a dedicated internal LAN device.)
Step 5: Test the Port Forwarding Rule.
Test: Use a public port checker tool online (such as https://www.yougetsignal.com/tools/open-ports/ ). Enter your home's public IP address (this will auto-fill using the example tool if you are using a device on the same network) and the external port number you configured.
If the tool reports the port is "Open" or "Active", your port forward is successful. If it reports "Closed" or "Timed Out", recheck your static IP (Step 3) and the rule configuration (Step 4). In some cases, the device and router may need to be powercycled for the change to take effect.